Flowers may be beautiful, but there are definitely a few out there that can pose serious risks to your pets. If you live with a dog, it’s crucial to know which plants are safe. The lily family (Liliaceae), which includes about 15 genera and roughly 610 species, is particularly concerning. While plants from two genera in this family, Lilium (True lilies) and Hemerocallis (Day lilies), are deadly toxic to cats, their toxicity in dogs remains unconfirmed. The level of toxicity to canines of plants in the Liliaceae family varies across species, with some being virtually harmless while others being highly poisonous. To complicate matters further, some plants that aren’t truly lilies still include the term ‘lily’ in their names, adding to the confusion.
We can definitively say that these plants are more toxic to cats than dogs because of their varying physiologies. The best advice we can offer is to avoid adding any lilies to your garden or as houseplants in your home if you have a pet. Prevention is by far the best cure.
Examples of Toxic Lily Species
Lilies as a group are diverse. We can say most species are perennial bulbs. Many species have showy flowers or are aromatic. Scientists refer to those of the Lilium genus as the true lilies. Many cultivars go by their scientific name, making knowing this information useful.
Dogs are vulnerable to accidental poisoning because of their eating habits. Many pups consume anything they find, making canines more likely to become victims. That’s why we recommend avoiding any lily plant altogether since most accidents occur in the pet’s home. As explained, the degree of toxicity varies with the species. For example, the Easter lily (Lilium longiflorum), which belongs to the Lilium genus, is not documented as toxic to dogs, but it is extremely toxic to cats.
Species of plants in the Liliaceae family that are toxic to dogs—and cats as well—through various toxins include the following:
- Tulip (Tulipa species)
- Hosta (Hosta plataginea)
- Climbing lily (Gloriosa superba)
- Lily of the valley (Convallaria majalisspp.)
- Lily of the palace or Barbados Lily (Hippeastrum)
Learning about the hosta, or plantain lily, surprised us, given how popular the plant is for landscaping. Hostas contain saponins, which cause gastrointestinal problems in dogs, cats, and horses after eating them. Notably, rabbits and deer can eat them without suffering any ill effects. Rutgers New Jersey Agricultural Experiment Station lists it as one of the least deer-resistant species. However, the takeaway is that toxicity varies with the animal. So, just because wildlife can eat a certain plant doesn’t mean it’s safe for your dog.
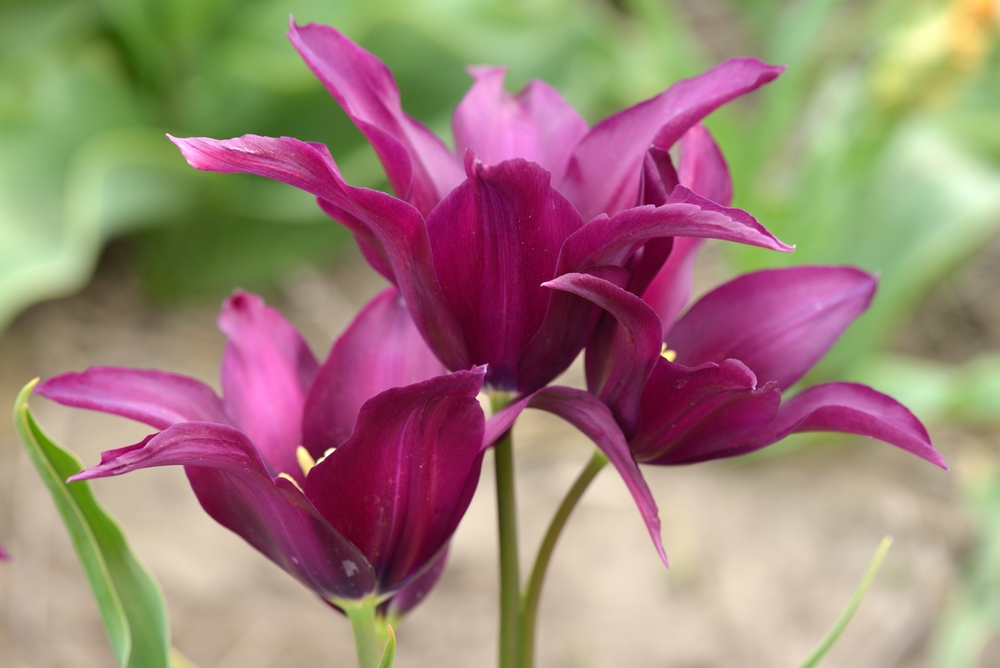

Other Species of Plants Called Lilies
There are a number of plants referred to as lilies but are actually members of different families. “Lily” has come to mean any similarly looking flower, and you’ll notice much variation in this list. Toxic species to dogs that do not belong to the Liliaceae family include the following:
- Lily of the valley (Convallaria majalis)
- Calla lily or Trumpet lily (Zantedeschia spp.)
- Wild daffodil or Lent lily (Narcissus pseudonarcissus)
- Lily of the palace or Barbados Lily (Hippeastrum)
- Peace lily (Spathiphyllum)
- Impala lily (Adenium obesum)
- Flamingo lily (Anthurium scherzeranum)
We’ve included the scientific names of all these species since many have several common names, further complicating their classification. Some plants have “spp.” after their genus name to indicate that many species exist under that umbrella, including many cultivars. Toxicity exists regardless of the individual species.


 Signs of Poisoning
Signs of Poisoning
The variety of plants on our list only scratches the surface of the issues with lilies. The signs of poisoning may also differ because of the specific toxin and its effects. For example, wild daffodils and lily of the palace contain a toxin called lycorine. This alkaloid is responsible for the signs of poisoning that follow the ingestion of this plant: vomiting, nausea, mouth irritation, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
One of the most common signs of poisoning is vomiting. A dog only needs to consume one bulb to show signs of toxicity. The toxin is mainly concentrated in the bulb, however ingestion of the leaves is equally worrisome.
Other plants, such as calla lily and peace lily, contain insoluble calcium oxalate crystals, which can cause mouth irritation when ingested or chewed.
These crystals can result in symptoms such as excessive drooling, difficulty swallowing, pawing at the mouth, vomiting, and swelling of the lips and tongue.
Lily of the valley poses a significant danger due to its toxins that can harm your pet’s cardiovascular system, with puppies and senior dogs being at the highest risk. Tulips are also highly toxic because of their tulipalin A and B content, leading to symptoms like drooling, vomiting, depression, and diarrhea. The bulbs contain the highest concentration of these chemicals, and there is no known antidote.
Common signs of toxicity include vomiting, drooling, diarrhea, loss of appetite, lethargy, abdominal pain, and seizures.
Prompt action is essential in cases of accidental poisoning, as many plants contain life-threatening toxins that can cause organ damage. Seek immediate veterinary assistance if you suspect your dog has ingested lilies or any poisonous plant.
Prevention is key in keeping your pets safe from toxic plants. Researching plant species and keeping them out of reach is crucial, as even bitter-tasting plants may not deter a curious or bored pet from ingesting them.
Choose pet-safe plants for your home and garden to avoid accidental poisoning and ensure the safety of your furry friends. following sentence:
The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.
Rewritten sentence: The fast brown fox leaps over the lethargic dog. following sentence:
“The cat jumped onto the counter and knocked over a glass vase.”
The cat leaped onto the counter and caused a glass vase to fall over.


